Delving into Gut health and its connection to brain function, this introduction immerses readers in a unique and compelling narrative. The intricate interplay between our gut health and brain function is a fascinating subject that has garnered increasing attention in recent years.
As we uncover the complexities of this relationship, a deeper understanding emerges of how our gut impacts not only our physical well-being but also our cognitive processes and emotional state.
As we navigate through the various factors that influence gut health and delve into the profound impact it has on our mental well-being, a clearer picture forms of the intricate mechanisms at play within our bodies.
Introduction to Gut Health and Brain Function
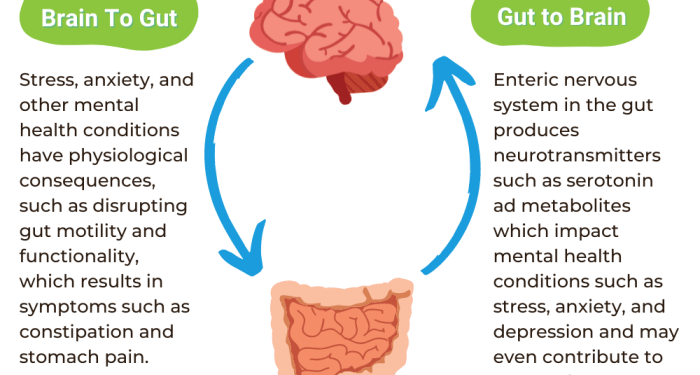
Gut health refers to the balance of microorganisms that reside in the gastrointestinal tract and play a crucial role in digestion, immunity, and overall health. The gut is often referred to as the "second brain" due to its significant impact on brain function and mental well-being.The concept of the brain-gut axis highlights the bidirectional communication between the gut and the brain.
This communication occurs through neural, hormonal, and immunological pathways, influencing various aspects of cognition, mood, and behavior.
Examples of How Gut Health Influences Brain Function
- 1. Serotonin Production: The majority of serotonin, a neurotransmitter that regulates mood, is produced in the gut. Imbalances in gut microbiota can affect serotonin levels, leading to mood disorders like depression.
- 2. Inflammation: Dysbiosis, an imbalance of gut bacteria, can trigger inflammation in the gut, which may contribute to neuroinflammation and neurological conditions such as Alzheimer's disease.
- 3. Stress Response: The gut microbiome can influence the body's response to stress by modulating the production of stress hormones like cortisol, impacting mental health and resilience.
The Role of the Microbiome in Gut-Brain Communication
The microbiome, a diverse community of microorganisms living in the gut, plays a crucial role in regulating the brain-gut axis. These microbes produce various compounds that can affect neurotransmitter levels, immune responses, and inflammation, ultimately shaping brain function and behavior.
Factors Influencing Gut Health
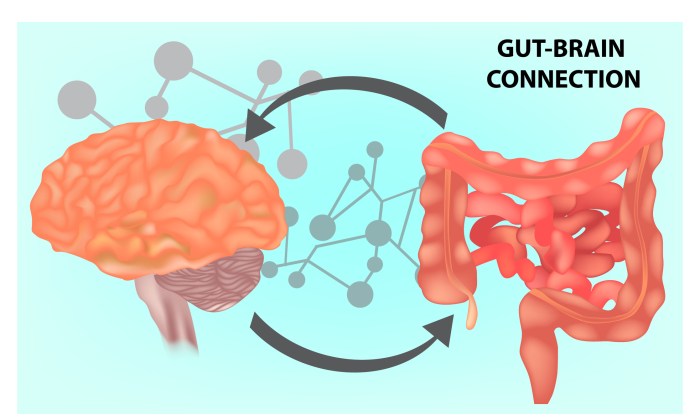
Maintaining a healthy gut is essential for overall well-being, as it plays a crucial role in various bodily functions. Several factors can influence gut health, including diet, probiotics, prebiotics, stress, and medications.
Diet Impact on Gut Health
A balanced diet rich in fiber, fruits, vegetables, and whole grains is crucial for a healthy gut. These foods promote the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut, supporting digestion and overall gut health.
Importance of Probiotics and Prebiotics
Probiotics are live bacteria that can benefit the gut by restoring the natural balance of bacteria. They can be found in fermented foods like yogurt and kimchi. Prebiotics, on the other hand, are non-digestible fibers that feed the good bacteria in the gut, promoting their growth and activity.
Effects of Stress on Gut Microbiota
Stress can have a significant impact on gut health by disrupting the balance of bacteria in the gut. Chronic stress can lead to inflammation and changes in gut motility, affecting digestion and nutrient absorption.
Medications and Gut Health
Certain medications, such as antibiotics, can disrupt the natural balance of bacteria in the gut by killing off both harmful and beneficial bacteria. This disruption can lead to digestive issues and other gut-related problems.
Gut Health and Mental Health
Gut health plays a crucial role in mental health, with growing evidence suggesting a strong connection between the two. The gut-brain axis, a bidirectional communication system, influences various mental health conditions.
Link between Gut Health and Mental Disorders
- Research has shown that imbalances in gut bacteria can contribute to mental disorders like depression and anxiety.
- Individuals with conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) often experience comorbid mental health issues, highlighting the gut-brain connection.
Role of Neurotransmitters in Gut-Brain Communication
- Neurotransmitters like serotonin, dopamine, and GABA produced in the gut play a vital role in regulating mood and behavior.
- Communication between the gut and the brain through neurotransmitters influences emotional well-being and mental health.
Gut Health Interventions for Mental Well-being
- Probiotics and prebiotics can help restore a healthy balance of gut bacteria, potentially improving symptoms of depression and anxiety.
- Dietary changes, such as incorporating more fiber-rich foods, can positively impact gut health and mental well-being.
Strategies to Improve Gut Health for Better Brain Function
Improving gut health can have a significant impact on brain function. Here are some strategies to enhance gut health for better cognitive health:
Dietary Changes that Promote a Healthy Gut
- Include a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins in your diet.
- Limit processed foods, sugar, and artificial additives.
- Consume foods rich in probiotics, such as yogurt, kefir, and sauerkraut.
- Increase fiber intake to support a healthy gut microbiome.
Benefits of Regular Exercise on Gut Health
Regular physical activity can positively impact gut health by:
- Reducing inflammation in the gut.
- Increasing diversity of gut microbes.
- Improving overall digestion and nutrient absorption.
Stress Management Techniques for a Healthier Gut
Effective stress management can improve gut health through:
- Practicing mindfulness meditation or deep breathing exercises.
- Engaging in regular physical activity to reduce stress levels.
- Seeking support from friends, family, or a mental health professional.
Tips for Maintaining a Balanced Gut Microbiome
To maintain a healthy balance of gut bacteria, consider:
- Avoiding unnecessary use of antibiotics.
- Eating prebiotic foods like garlic, onions, and bananas.
- Limiting exposure to environmental toxins that can disrupt the microbiome.
Ultimate Conclusion
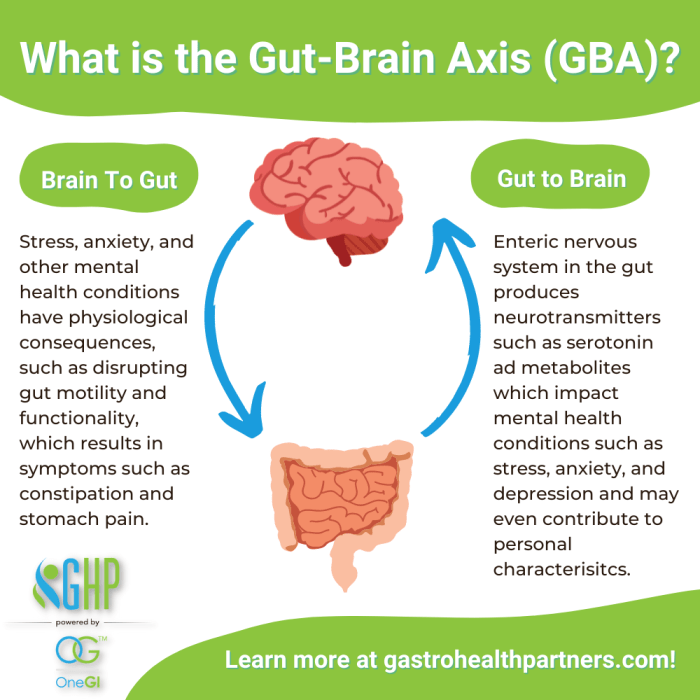
In conclusion, the connection between gut health and brain function is a multifaceted and dynamic one that continues to intrigue researchers and health enthusiasts alike. By recognizing the vital role our gut plays in shaping our cognitive functions and emotional balance, we are empowered to make informed choices that benefit not only our physical health but also our mental well-being.
As we strive to optimize our gut health, we pave the way for enhanced brain function and overall vitality.
Essential FAQs
How does gut health influence brain function?
Our gut health impacts brain function through the intricate brain-gut axis, where the microbiome communicates with the brain via various pathways, influencing cognitive processes and emotional well-being.
Can probiotics improve mental health?
Probiotics have shown promising results in supporting mental health by promoting a healthy gut microbiome, which in turn positively impacts neurotransmitter production and mood regulation.
What role do neurotransmitters play in gut-brain communication?
Neurotransmitters act as chemical messengers that facilitate communication between the gut and brain, influencing mood, cognition, and overall mental health.
How can dietary changes promote a healthy gut?
Adopting a diet rich in fiber, fermented foods, and healthy fats can support gut health by nourishing beneficial gut bacteria and promoting a balanced microbiome.